
Doctors understand the general brain areas responsible for these activities, but fMRI can help pinpoint them more precisely.ĭuring fMRI of the brain, the technologist will ask the patient to perform a specific task, such as naming objects, which illuminates active areas of the brain. Radiologic tests include: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)Ī brain MRI allows a physician to clearly see a patient’s internal body structures, including brain tissue, using magnetic fields and radio waves.īy revealing details of the brain’s structure in cross-sectional images called “cuts,” MRI can help the doctor locate possible seizure-producing areas in or next to the regions of structural change (called a seizure focus in patients with focal epilepsy or foci in patients with multifocal epilepsy).ĭiagnostic protocols for epilepsy may involve a 3-D portion and special coronal cuts so the epilepsy specialist can evaluate the temporal lobes for signs of mesial temporal sclerosis or malformation of a part of the brain called the hippocampus.Ī brain MRI may not be necessary or indicated in patients with generalized epilepsy (seizures coming from the entire brain at once rather than focal or multifocal areas).įunctional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) of the brain can help locate areas where speech, memory, movement or other functions take place. Some of these issues can be treated with epilepsy surgery. Some seizures and epilepsies are due to irregularities within the brain tissue, such as scars, tumors or other lesions that can show up on radiologic imaging. Prolonged video-EEG monitoring uses a video camera to capture onset and characteristics of seizures simultaneously with an EEG. Prolonged EEGs: If a routine EEG is normal, diagnosing seizures may require a stay in an epilepsy monitoring unit for continuous EEG monitoring with video over several days. Clinicians can find evidence of abnormal electrical activity in the brain and figure out the type or types of seizures a patient is having, as well as the origin(s), by measuring brain waves over minutes to a couple of hours.
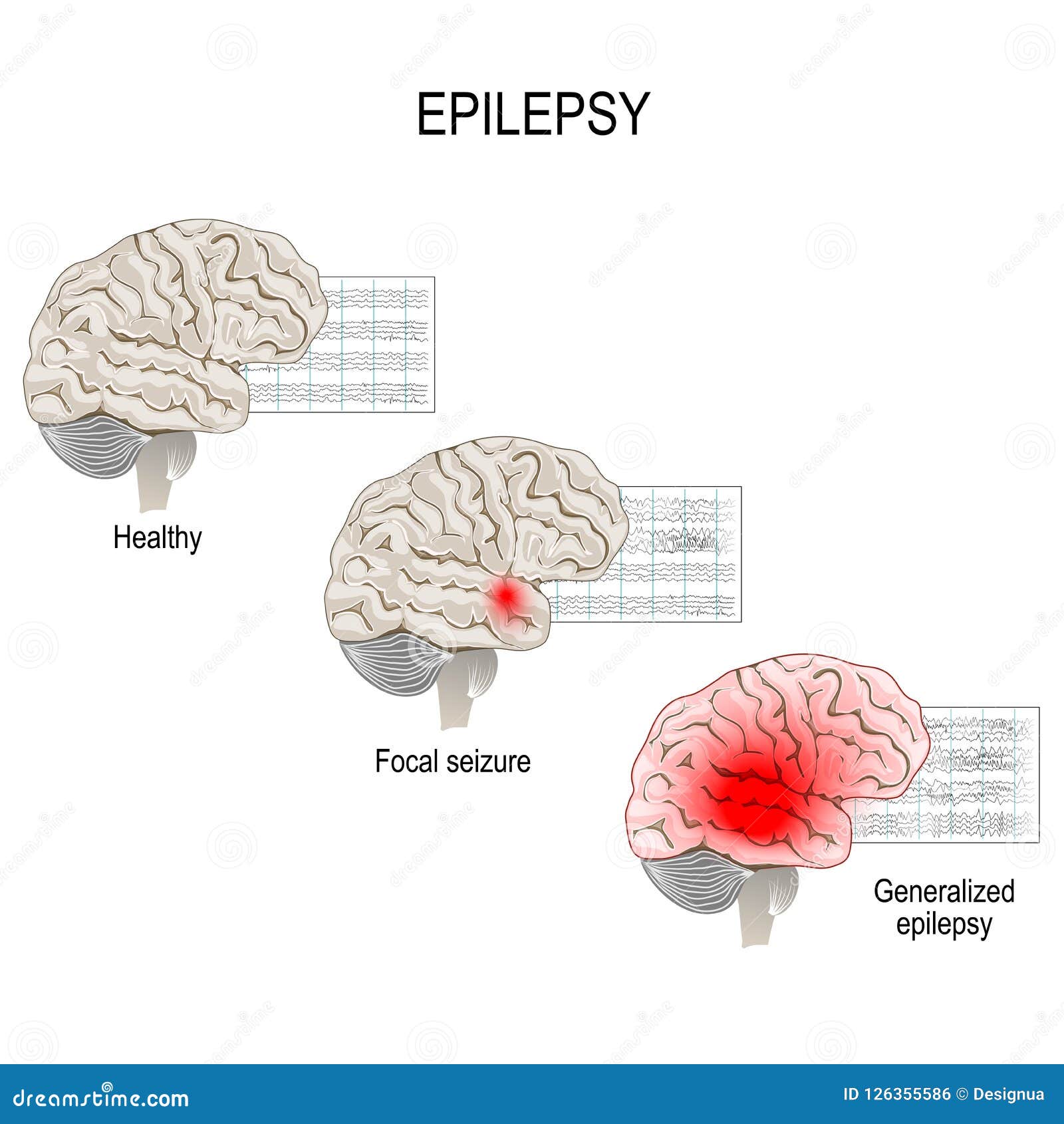
These studies are interpreted, or “read,” by a trained neurologist. Routine EEG: Monitoring of electrical signals in the brain with electrodes (sensors) attached to the scalp is usually first performed in a specialized outpatient clinic.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
